Leading EMIs in Europe 2023: Navigating the Dynamic Fintech Landscape

Top 10 EMIs in Europe 2023
Over the last five years, the world of fintech (financial technology) has been incredibly dynamic. As of 2023, there are about 650 companies in Europe known as electronic money institutions (EMIs), making it a busy marketplace. However, this field is also extremely competitive. Surprisingly, up to 10% of these financial institutions have faced challenges, leading some to close or go bankrupt. There are several reasons for this, such as not passing regulatory audits, lacking proper management, or trying to grow too fast without the right foundation. Some turned into soap bubbles, starting strong but quickly bursting. In this article, we’ll introduce you to the top 10 EMIs in Europe that have not just survived this tough competition but have thrived, showing their resilience and innovation in a constantly changing financial world.
Top 10 EMI-Licensed Neobanks in Europe 2023
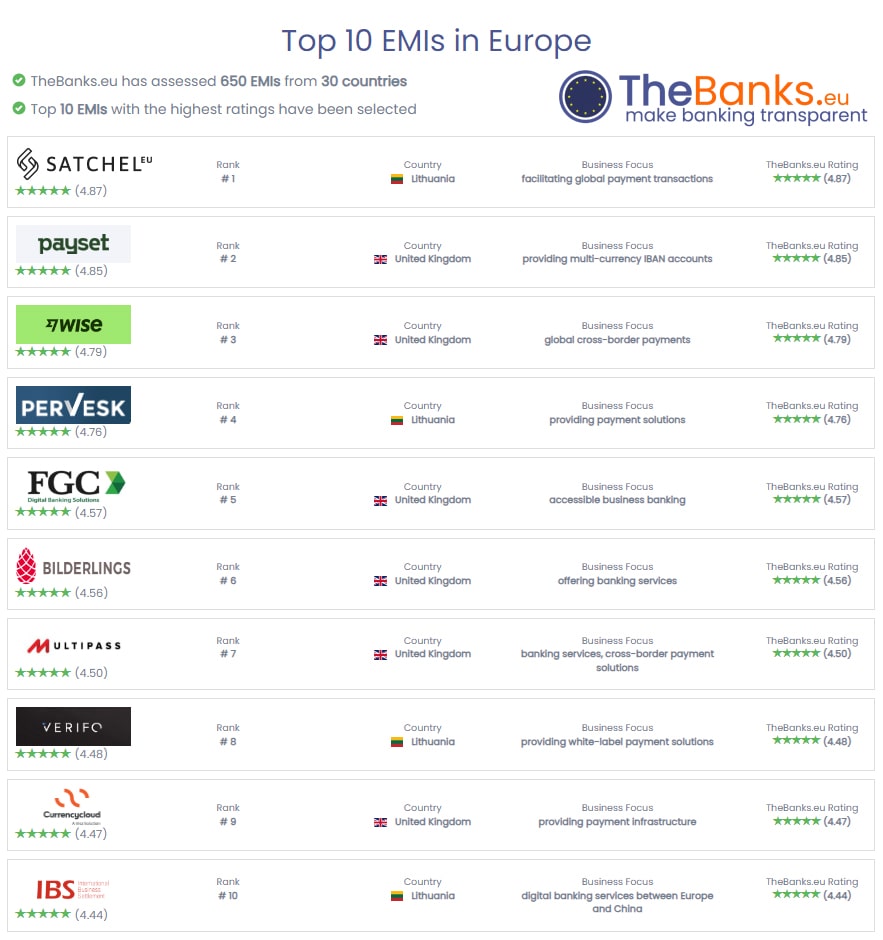
TheBanks.EU, an independent European financial portal with a track record dating back to 2012, conducts comprehensive and impartial evaluations, rigorously testing the services, pricing, and user-friendliness of various banks and EMIs. According to their independent rankings, the coveted “Top 10 EMIs in Europe” list is spearheaded by Satchel.eu, a Lithuanian-based neobank that entered the financial services market in 2018. Following closely behind, the British digital banking operator Payset takes the second spot, with the fintech giant Wise securing the third position. Notably, Lithuanian institution Perversk and British FGC round out the top 5 contenders. The complete list can be found below or by accessing the provided link:
What Are EMIs?
Electronic money institutions (EMIs) are modern digital entities that provide a range of financial services. EMIs operate under the oversight of the same local financial regulatory authorities as traditional banks, with the EMI license primarily granted by the respective national bank. For users, digital banking with an EMI is as easy and convenient as with a traditional bank, as the former offer user-friendly apps and accessible web client offices.
EMIs, often called neobanks, enable digital (e-money) transactions on behalf of their customers. Typically, EMIs operate predominantly online, as their name suggests. However, some EMIs may also maintain physical branches, allowing in-person visits similar to traditional banks. The rise of EMIs in Europe commenced around 2009, with the introduction of the Directive 2009/110/EC, commonly known as the E-Money Directive, which authorized the operation of EMIs. Nowadays, this type of banking is in its prime.
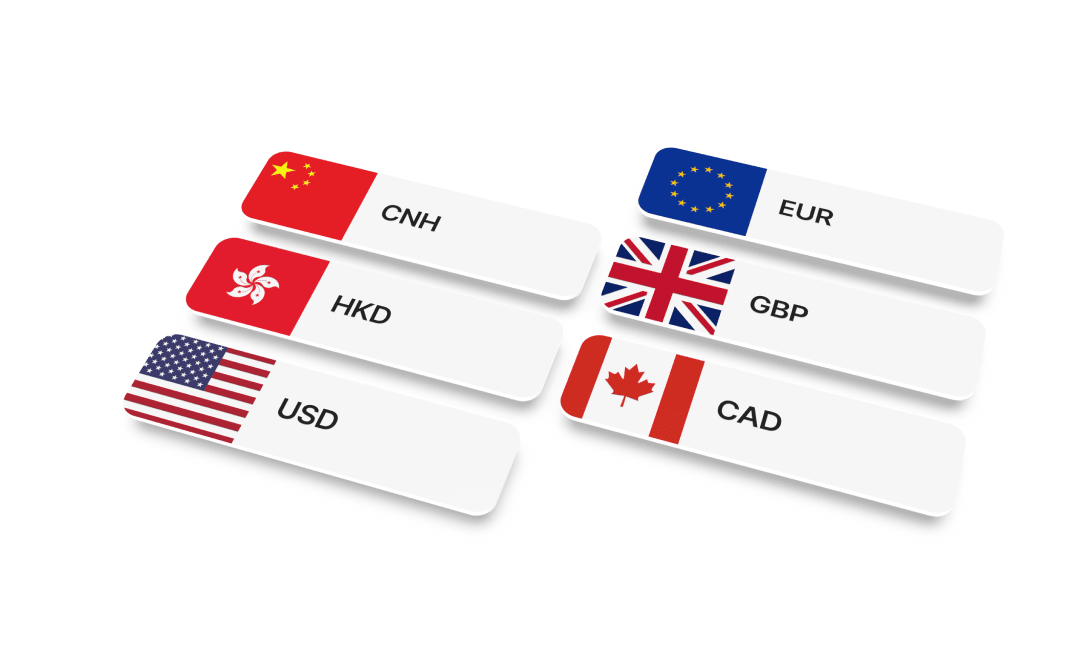
While EMIs offer a more limited scope of services compared to fully licensed banks, they excel in facilitating both local and international payments. This ability makes cross-border and local transactions more convenient and cost-effective for individuals and businesses than traditional banking methods. EMIs specialize in straightforward IBAN account opening and e-money transactions. They encompass tasks such as currency transfer, storage (often in multiple currencies), foreign exchange, prepaid and debit card services, and e-wallets. Additionally, EMIs may provide valuable features like multi-currency accounts, payment cards, and more.
Given the international nature of their services, EMIs often manage transfers across various networks, including SEPA, SWIFT, CHAPS, EFT, Faster Payments, and ACH. It’s essential to recognize that, as online banking evolves, traditional banks now offer similar online payment services to those provided by EMIs. Consequently, many digital payment services are accessible through conventional banks. However, it’s crucial to note that EMIs do not provide certain critical features found in banks, such as lending or investment services. Put simply, they do not issue credit cards or offer investment advice.








